|
& Cone Frustum Calculator
It can now solve for cones if you know 2 out of these 4 variables: RADIUS HEIGHT SLANT HEIGHT SLANT ANGLE
First choose cone or frustum: (These buttons work ONLY with cones and NOT frustums.)
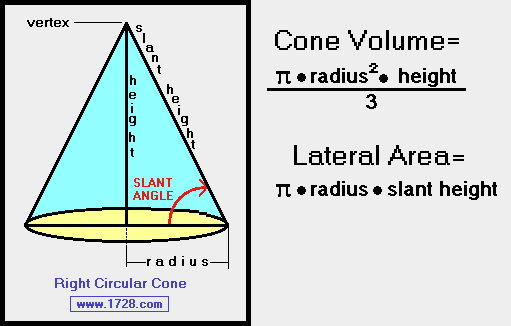
A right circular cone is a geometric solid formed by all lines drawn from a circular base and terminating at a common point called the vertex, which is located above the center of the circular base. A perpendicular line drawn from the vertex to the center of the base is called the height of the cone. The formula for finding circular area has already been discussed on this site as well as the Pythagorean Theorem which can be used to calculate slant height.
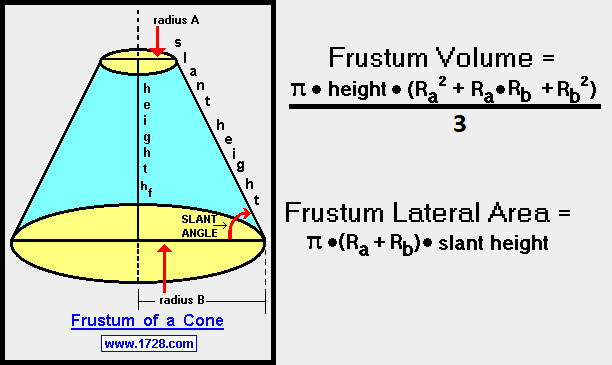
A frustum
(sometimes incorrectly spelled frustrum)
of a right circular cone is that part of a right
circular cone between the base of the cone and a plane which intersects the cone parallel to
the base.
There are formulas for frustums, but if you think about it, the
calculations can be done by extending the frustum height to a vertex and
then subtracting the "upper" cone's values from the complete (or extended) cone yielding the
values for the frustum.
If we call 'Radius A' Ra
'Radius B' Rband the frustum height
hf then the "upper cone height" hu is found by:
and the height of the extended cone is (hu + hf). From there you can calculate the volumes and areas of each cone and subtract the upper cone values from the extended cone to find the frustum values. For those who'd still like to see the frustum formulas, here they are:
Yes you could use these formulas for cone calculations. However, as
you know, here at "1728", there's always a calculator to do the work
for you.
The default setting is for 5 significant figures but you can change that
by inputting another number in the box above.
|